전자공학 및 알고리즘
백준 2842 - 집배원 한상덕(C++) 본문
문제 링크입니다. https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2842
2842번: 집배원 한상덕
상덕이는 언덕 위에 있는 마을의 우체국에 직업을 얻었다. 마을은 N×N 행렬로 나타낼 수 있다. 행렬로 나뉘어진 각 지역은 우체국은 'P', 집은 'K', 목초지는 '.' 중 하나로 나타낼 수 있다. 또, 각
www.acmicpc.net
BFS와 이분 탐색을 사용해야하는 문제였습니다.

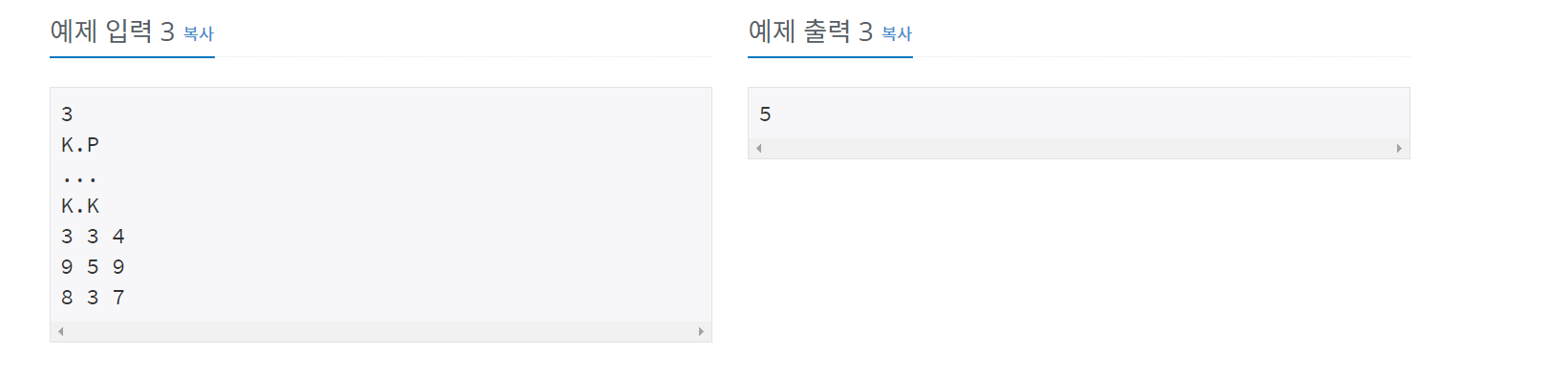
N*N 배열에서 모든 편지를 전달하고 돌아올 때, 최소 피로도를 구하는 문제였습니다.
저는 N*N 배열의 값을 백터를 통해서 저장하고 정렬한 후 중복된 값을 전부 없앤 뒤, 범위를 (0 ~ 1), (0 ~ 2) 등으로 늘려가면서 이동할 수 있는 경로가 있는지를 확인했습니다.
출력 예시 - 예제 입력 3을 통해서 설명하겠습니다.

문제 접근 방법
1. N*N 배열의 값을 백터의 담은 후, 정렬과 중복 제거를 한다.
2. Low = 0, Low < tire.size() 의 값보다 작을 때 까지 Low와 High의 값을 바꾸면서 탐색한다.
3. tire[Low] ~ tire[High] 사이의 값을 통해서 전달을 할 수 있을 경우, 피로도를 계산하여 비교한다.
4. 전달할 수 없을 경우, High의 값을 1 증가한다. -> tire.size() 보다 크기가 커지면 안됩니다.
5. 탐색을 마친 후, 최소 피로도를 출력한다.
이때, 돌아가는 길은 확인을 안해도 됩니다. 한 경로로만 이동할 수 있도록 만들었기에, 같은 결과값이 나와 굳이 확인할 필요는 없습니다.
문제 접근 방법 - 1번 + 2번 (solve() 함수)
sort(tire.begin(), tire.end());
tire.erase(unique(tire.begin(), tire.end()), tire.end());위와 같은 코드를 통해서 정렬 후 중복 제거를 할 수 있습니다.
자세한 것은 코드를 참고해주세요!
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int N;
char miro[51][51];
int slope[51][51];
int check[51][51];
int dx[8] = { 1,0,-1,0,1,1,-1,-1 };
int dy[8] = { 0,1,0,-1,1,-1,-1,1 };
vector<int> tire;
pair<int, int> start;
int house = 0;
int bfs(int low, int high) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
if (slope[start.first][start.second] >= tire[low] && slope[start.first][start.second] <= tire[high]) {
q.push(make_pair(start.first, start.second));
check[start.first][start.second] = 1;
}
int visit = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().first;
int y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int xx = x + dx[i];
int yy = y + dy[i];
if (xx >= 1 && yy >= 1 && xx <= N && yy <= N) {
if (check[xx][yy] == 0 && slope[xx][yy] >= tire[low] && slope[xx][yy] <= tire[high]) {
check[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push(make_pair(xx, yy));
if (miro[xx][yy] == 'K') visit++;
}
}
}
}
if (visit == house) {
return 1;
}
else return 2;
}
void solve() {
sort(tire.begin(), tire.end());
tire.erase(unique(tire.begin(), tire.end()), tire.end());
int low = 0;
int high = 0;
int result = 987654321;
while (low < tire.size()) {
memset(check, 0, sizeof(check));
int ans = bfs(low, high);
if (ans == 1) {
result = min(result, tire[high] - tire[low]);
low++;
}
else {
if (high < tire.size() - 1) high++;
else break;
}
}
cout << result;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
cin >> miro[i][j];
if (miro[i][j] == 'P') {
start.first = i;
start.second = j;
}
else if (miro[i][j] == 'K') house++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
cin >> slope[i][j];
tire.push_back(slope[i][j]);
}
}
solve();
return 0;
}

질문 및 조언 댓글 남겨주세요!
'백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 11049 - 행렬 곱셈 순서(C++) (3) | 2021.10.28 |
|---|---|
| 백준 11066 - 파일 합치기(C++) (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| 백준 1981 - 배열에서 이동(C++) (0) | 2021.10.24 |
| 백준 2479 - 경로 찾기(C++) (0) | 2021.10.23 |
| 백준 16926 - 벽 부수고 이동하기 4(C++) (0) | 2021.10.09 |




